
A new study published by Unanimous AI finds that groups reach optimal decisions at significantly higher rates using Swarm Technology than by traditional voting
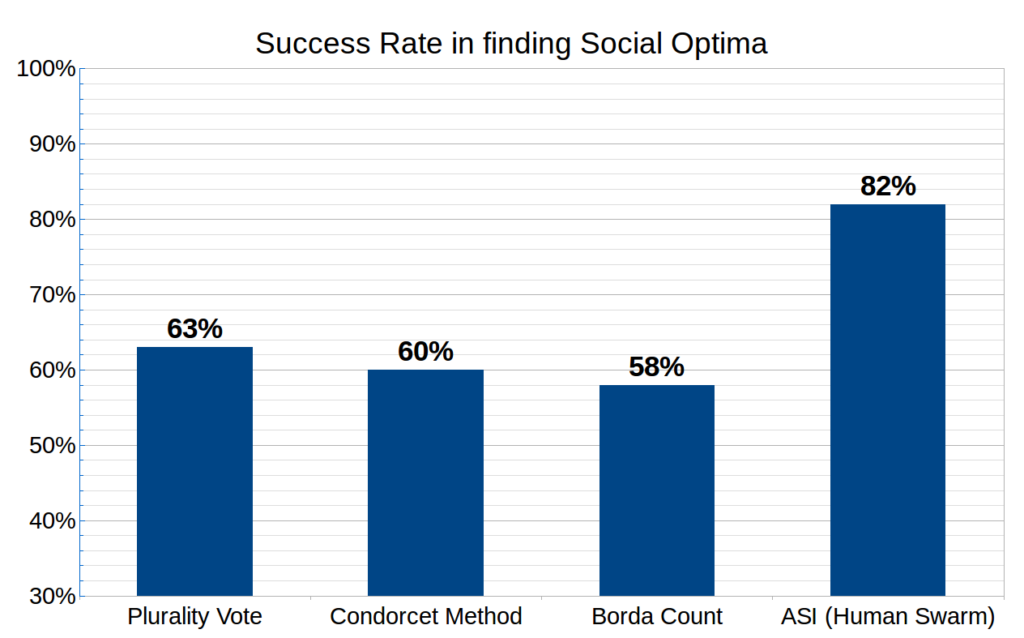
Today, Unanimous AI published a study concluding that groups are significantly more effective at reaching optimal decisions when deliberating as online “swarms” as compared to using traditional voting methods. The new study, entitled “Artificial Swarms Find Social Optima,” compares groups connected by Swarm AI technology to groups using three common voting methods (Plurality Vote, Ranked Voting, and Pairwise Voting) and finds that swarming enables groups to reach optimal decisions 36% more often than when taking a traditional vote.
Inspired by the remarkable abilities of schooling fish, flocking birds, and swarming bees to converge on optimal decisions, Swarm AI technology enables human teams to form similar systems online. Prior research has shown that swarming can amplify the intelligence of networked groups, enabling teams to make significantly more accurate predictions, forecasts, and estimation. This new study is the first to show that groups working as online swarms can reach optimal decisions as well.
“Conducting votes and polls has been the cornerstone of group decision-making for hundreds of years, but it often leads to outcomes that do not represent the collective interests of the population,” says Dr. Louis Rosenberg, CEO of Unanimous AI. “This new research suggests there is a better way for groups to reach effective decisions, and it’s rooted in a far deeper history – evolution – which has empowered other social species to form systems that converge on decisions in unison.”
This research falls in the field of Social Choice Theory, which studies how groups with conflicting interests can reach decisions that optimize the welfare of populations. In the 18th century, Nicolas de Condorcet observed that even if individual voters are all rational, plurality voting can lead to irrational outcomes. In response, many alternate voting methodologies were developed, including ranked voting and pairwise voting, also known as Borda Count and the Condorcet Method. Each of these methods has their strengths, but all fail to reach optimal decisions at significant rates.
In the study published today, researchers compared decisions made by groups working as online swarms, with three common voting strategies (Plurality Vote, Condorcet Method, and Borda Count). Across a set of 100 test questions designed to illicit conflicting interests within the groups, results demonstrated a significant advantage for swarming as compared to traditional voting methods.
The paper, “Artificial Swarms Find Social Optima,” will be presented by Dr. Louis Rosenberg at the Conference on Cognitive and Computational Aspects of Situation Management (CogSIMA 2018) on June 13th in Boston, MA. A pre-release version can be downloaded here.
About Unanimous AI
Unanimous AI is a Silicon Valley company that has pioneered Swarm AI® technology, a new form of AI that combines real-time human insights and AI algorithms modeled after natural swarms. Unanimous has generated an impressive track record of predictions, forecasts and insights. The company’s technology has outperformed traditional AI systems and human experts in many high-profile challenges.
Unanimous works with corporate clients and leading organizations through its Swarm Insight® business intelligence service. Swarm Insight helps clients amplify the intelligence of consumer groups as well as amplify the intelligence of business teams to help make better decisions.
In 2018, Swarm AI was recognized as SXSW’s “Artificial Intelligence Innovation of the Year” and was described in a popular TED TALK here. For more about Unanimous A.I., visit http://unanimous.ai
Unanimous will be fielding swarms throughout 2018 to track the sentiment of the American public and to identify the trends and behaviors that are shaping our future. If you would like to stay informed of our research, sign up below.
Want to learn more about our Swarm AI technology? Check out our TED talk below…

